CueNIMBY user guide
Complete guide to using CueNIMBY for workstation control
This guide covers all aspects of using CueNIMBY, OpenCue’s system tray application for workstation NIMBY control.
Table of contents
- CueNIMBY user guide
Overview
CueNIMBY is a Qt-based cross-platform system tray application that gives you control over your workstation’s availability for rendering. Built with Qt6 for native look and feel, it features professional icons with the OpenCue logo. It provides:
- Visual feedback: Professional icons with OpenCue logo showing distinct states
- Enhanced status detection: Monitors CueBot connectivity, host registration, and ping times
- Emoji hints: Quick status recognition with 🔒❌⚠️🔧 in notifications
- Manual control: Toggle rendering on/off with intelligent menu states
- Desktop notifications: Alerts with helpful troubleshooting information when jobs start or state changes
- Quick access to CueGUI: Launch CueGUI directly from the tray menu
- Config file editing: Open configuration file directly from tray
- Resilient connection: Starts even when CueBot is unreachable and reconnects automatically
- Time-based scheduling: Automatic state changes based on your schedule
- Cross-platform support: Works on macOS, Windows, and Linux with native UI
Installation
Requirements
- Python 3.7 or later
- Qt for Python (PyQt6 or PySide6) - automatically installed with CueNIMBY
- OpenCue client libraries (pycue)
- Access to a Cuebot server (CueNIMBY will start even if CueBot is unreachable)
Installing from source
cd OpenCue/cuenimby
pip install .
Verifying installation
cuenimby --version
Getting started
Starting CueNIMBY
Launch CueNIMBY from the command line:
cuenimby
The application starts in the background and adds an icon to your system tray.
Connecting to Cuebot
Using command-line options
cuenimby --cuebot-host cuebot.example.com --cuebot-port 8443
Using environment variables
export CUEBOT_HOST=cuebot.example.com
export CUEBOT_PORT=8443
cuenimby
Using configuration file
Create or edit ~/.opencue/cuenimby.json:
{
"cuebot_host": "cuebot.example.com",
"cuebot_port": 8443
}
Understanding the tray icon
The CueNIMBY tray icon uses professional icons with the OpenCue logo to indicate your workstation’s current state. All icons are designed for clarity at small sizes and provide consistent visual identity.
macOS - Available state example:
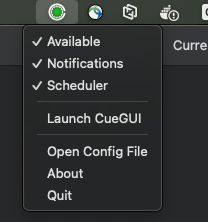
Windows - Available state example:
| Icon File | Emoji | State | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
opencue-starting.png |
🔄 | Starting | Application is initializing |
opencue-available.png |
🟢 | Available | Your machine is idle and ready to accept rendering jobs |
opencue-working.png |
🔴 | Working | Your machine is currently rendering a frame (red dot in center) |
opencue-disabled.png |
🔴 | Disabled | You’ve manually disabled rendering via CueNIMBY or CueGUI |
opencue-disabled.png |
🔒 | NIMBY Locked | RQD has locked the machine due to user activity |
opencue-disabled.png |
❌ | Host Down | RQD is not running on the host |
opencue-error.png |
❌ | CueBot Unreachable | Cannot connect to CueBot server - CueNIMBY will reconnect automatically |
opencue-error.png |
❌ | No Host | Machine not found on CueBot - check if RQD is running |
opencue-warning.png |
⚠️ | Host Lagging | Host ping above 60 second limit - check if RQD is running |
opencue-repair.png |
🔧 | Repair | Host is under repair - contact tech team |
opencue-unknown.png |
❓ | Unknown | Cannot determine state |
Icon Gallery
All CueNIMBY icons feature the OpenCue logo for professional appearance and consistent visual identity:
| Icon | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
opencue-available.png |
Green icon - Host ready for rendering | |
opencue-working.png |
Icon with red dot in center - Currently rendering | |
opencue-disabled.png |
Red icon - Host locked/disabled | |
opencue-error.png |
Red X icon - Connection error | |
opencue-warning.png |
Yellow icon - Warning state | |
opencue-repair.png |
Orange icon - Under repair | |
opencue-starting.png |
Gray icon - Initializing | |
opencue-unknown.png |
Gray ? icon - Unknown state | |
opencue-default.png |
Default fallback icon |
State transitions
Available ⟷ Working
↕ ↕
Disabled ⟷ NIMBY Locked
- Available ↔ Working: Happens automatically when jobs start/finish
- Available ↔ Disabled: You control via the menu
- Any → NIMBY Locked: RQD detects user activity
- NIMBY Locked → Available: RQD detects idle period
Using the menu
Right-click the CueNIMBY icon to open the menu.
Available (checkbox)
Controls whether your machine accepts rendering jobs.
Checked (🟢/🔴): Machine is available for rendering
- Jobs can be dispatched to your machine
- Currently running jobs continue
Unchecked (🔴): Machine is disabled for rendering
- No new jobs will be dispatched
- Currently running jobs are killed (unless they have
ignore_nimby=true)
Intelligent menu state: This option is automatically disabled when:
- CueBot is unreachable (❌ icon)
- Host is not found on CueBot (❌ icon)
- Connection issues prevent state changes
To toggle:
- Right-click the tray icon
- Click “Available” to check/uncheck (if enabled)
Notifications (checkbox)
Controls desktop notifications with emoji hints (🔒❌⚠️🔧) for quick status recognition.
Checked: Notifications enabled
- Alert when a rendering job starts
- Alert when NIMBY locks/unlocks
- Alert when you manually change availability
- Alert when CueBot is unreachable with troubleshooting guidance
- Alert when host is not found with RQD status hints
- Warning when host is lagging
- Notification when host is under repair
Unchecked: Notifications disabled
- No desktop alerts
- Icon still updates to show state
To toggle:
- Right-click the tray icon
- Click “Notifications” to check/uncheck
Scheduler (checkbox)
Controls time-based automatic state changes.
Checked: Scheduler active
- Your machine automatically changes state based on schedule
- Example: Disabled 9am-6pm Mon-Fri, available otherwise
Unchecked: Scheduler inactive
- No automatic state changes
- You maintain full manual control
To toggle:
- Right-click the tray icon
- Click “Scheduler” to check/uncheck
See Scheduler section for configuration details.
Launch CueGUI
Opens CueGUI application directly from the tray for convenient access to the full OpenCue interface.
macOS:
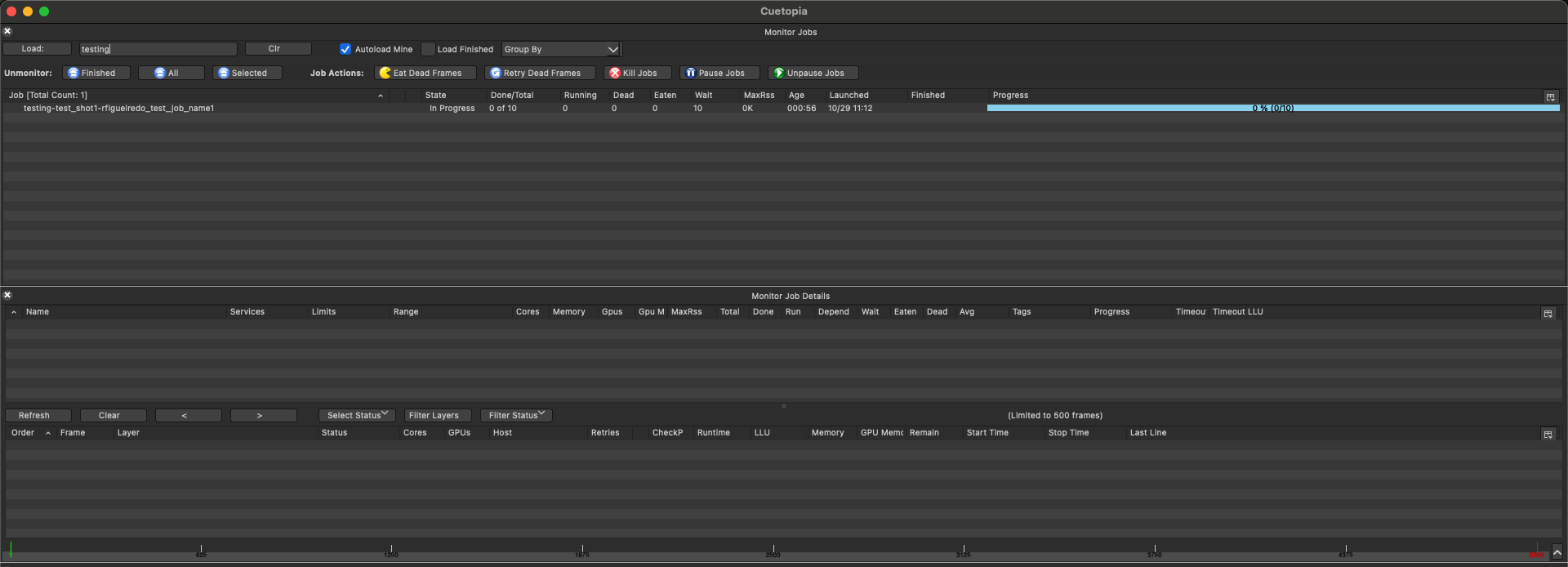
Availability: This option is automatically disabled when CueGUI is not available on your system.
To use:
- Right-click the tray icon
- Click “Launch CueGUI”
This feature provides quick workflow improvement for accessing detailed job information, host management, and other CueGUI features.
Open Config File
Opens the configuration file (~/.opencue/cuenimby.json) in your default editor.
macOS:
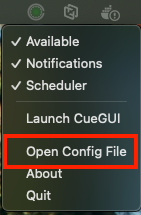
To use:
- Right-click the tray icon
- Click “Open Config File”
- Make your changes
- Restart CueNIMBY for changes to take effect
About
Shows application information using Qt dialog:
- CueNIMBY version
- CueBot server address (e.g., cuebot.example.com:8443)
- Host being monitored (your hostname)
- Brief description
macOS:
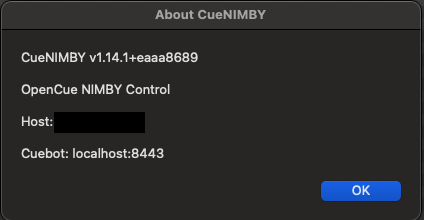
The enhanced About dialog includes connection information for troubleshooting and helps verify your configuration.
Quit
Exits CueNIMBY. Your machine’s state in OpenCue remains unchanged.
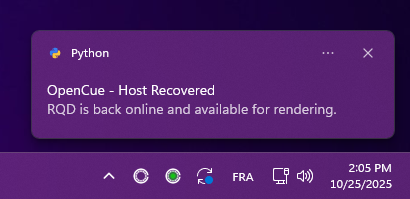
Desktop notifications
CueNIMBY sends desktop notifications for important events.
Notification types
Frame Started
OpenCue - Frame Started
Rendering: myshow_ep101/frame_0001
Sent when a rendering job begins on your machine.
NIMBY Locked
OpenCue - NIMBY Locked
Host locked due to user activity. Rendering stopped.
Sent when RQD detects user activity and locks the machine.
NIMBY Unlocked
OpenCue - NIMBY Unlocked
Host available for rendering.
Sent when RQD unlocks after an idle period.
Host Disabled
OpenCue - Host Disabled
Host manually disabled for rendering.
Sent when you manually disable rendering.
Host Enabled
OpenCue - Host Enabled
Host enabled for rendering.
Sent when you manually enable rendering.
CueBot Unreachable
❌ OpenCue - CueBot Unreachable
Cannot connect to CueBot server. Check connection.
Sent when CueNIMBY cannot connect to the CueBot server. Includes troubleshooting guidance. CueNIMBY will continue running and automatically reconnect when CueBot becomes available.
Host Not Found
❌ OpenCue - Host Not Found
Machine not found on CueBot. Check if RQD is running.
Sent when the monitored host is not registered with CueBot. Includes hints to check RQD status.
Host Lagging
⚠️ OpenCue - Host Lagging
Host ping above limit. Check if RQD is running.
Sent when host ping exceeds 60 seconds, indicating potential connection or RQD issues.
Host Under Repair
🔧 OpenCue - Under Repair
Host is under repair. Contact tech team.
Sent when host has been administratively marked for repair. No rendering will occur until cleared.
Platform-specific behavior
macOS:
- Uses native Notification Center
- Notifications appear in top-right corner
- Requires notification permissions (granted on first notification)
- Auto-detects and uses
terminal-notifierif available (most reliable) - Fallback chain: terminal-notifier → pync → osascript
- For best results, install terminal-notifier:
brew install terminal-notifier
Windows:
- Uses Windows 10+ toast notifications
- Notifications appear in bottom-right corner
- Respects Windows notification settings
Linux:
- Uses freedesktop notification standard
- Appearance depends on desktop environment
- Requires notification daemon (usually pre-installed)
Disabling notifications
Temporarily:
- Right-click tray icon
- Uncheck “Notifications”
Permanently:
Edit ~/.opencue/cuenimby.json:
{
"show_notifications": false
}
Scheduler
The scheduler automatically controls your machine’s availability based on time and day of week.
How scheduling works
- Define time periods for each day of the week
- Specify desired state during those periods
- CueNIMBY automatically changes state based on current time
- Outside scheduled periods, opposite state applies
Configuration
Edit ~/.opencue/cuenimby.json:
{
"scheduler_enabled": true,
"schedule": {
"monday": {
"start": "09:00",
"end": "18:00",
"state": "disabled"
},
"tuesday": {
"start": "09:00",
"end": "18:00",
"state": "disabled"
},
"wednesday": {
"start": "09:00",
"end": "18:00",
"state": "disabled"
},
"thursday": {
"start": "09:00",
"end": "18:00",
"state": "disabled"
},
"friday": {
"start": "09:00",
"end": "18:00",
"state": "disabled"
}
}
}
Schedule format
Each day entry contains:
- start: Start time in HH:MM format (24-hour)
- end: End time in HH:MM format (24-hour)
- state: Desired state during this period
"disabled": Machine will be locked"available": Machine will be unlocked
Schedule examples
Example 1: Workday protection
Disable rendering during business hours:
"monday": {
"start": "09:00",
"end": "18:00",
"state": "disabled"
}
- 9am-6pm: Disabled
- 6pm-9am: Available
Example 2: Lunch hour
Enable rendering during lunch:
"monday": {
"start": "12:00",
"end": "13:00",
"state": "available"
}
Example 3: Night shift
Disable during night shift:
"monday": {
"start": "22:00",
"end": "06:00",
"state": "disabled"
}
Example 4: Weekend availability
No entry = always use manual control on weekends.
Enabling the scheduler
Via menu:
- Configure schedule in config file
- Right-click tray icon
- Check “Scheduler”
Via config file:
{
"scheduler_enabled": true
}
Scheduler behavior
- Checks schedule every minute
- Changes state if needed
- Shows notification when changing state
- Manual changes override scheduler until next check
- Disabled days use manual control
Configuration
Configuration file location
~/.opencue/cuenimby.json
On first run, CueNIMBY creates this file with default values.
Full configuration example
{
"cuebot_host": "cuebot.example.com",
"cuebot_port": 8443,
"hostname": null,
"poll_interval": 5,
"show_notifications": true,
"notification_duration": 5,
"scheduler_enabled": true,
"schedule": {
"monday": {
"start": "09:00",
"end": "18:00",
"state": "disabled"
}
}
}
Configuration options
| Option | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
cuebot_host |
string | “localhost” | Cuebot server hostname |
cuebot_port |
integer | 8443 | Cuebot server port |
hostname |
string/null | null | Host to monitor (null = auto-detect) |
poll_interval |
integer | 5 | State check interval (seconds) |
show_notifications |
boolean | true | Enable desktop notifications |
notification_duration |
integer | 5 | Notification display time (seconds) |
scheduler_enabled |
boolean | false | Enable time-based scheduler |
schedule |
object | {} | Weekly schedule configuration |
Reloading configuration
Changes to the config file take effect:
- Immediately for most settings
- After restart for connection settings
To apply connection changes:
- Quit CueNIMBY
- Edit config file
- Restart CueNIMBY
Command-line options
Basic usage
cuenimby [OPTIONS]
Available options
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
--version |
Show version and exit |
--config PATH |
Path to config file |
--cuebot-host HOST |
Cuebot hostname (overrides config) |
--cuebot-port PORT |
Cuebot port (overrides config) |
--hostname HOST |
Host to monitor (default: local) |
--no-notifications |
Disable notifications |
--verbose, -v |
Enable verbose logging |
Examples
Connect to specific Cuebot:
cuenimby --cuebot-host cuebot.prod.example.com --cuebot-port 8443
Monitor different host:
cuenimby --hostname workstation-02
Disable notifications:
cuenimby --no-notifications
Debug mode:
cuenimby --verbose
Custom config:
cuenimby --config /path/to/custom/config.json
Integration with RQD
CueNIMBY works alongside RQD’s automatic NIMBY feature.
For detailed information on how NIMBY states interact with desktop rendering allocations and show subscriptions, see the Desktop rendering control guide.
How they work together
RQD (Automatic):
- Monitors keyboard/mouse input
- Locks immediately on user activity
- Unlocks after idle period (default 5 minutes)
- Kills running frames when locking
CueNIMBY (Manual + Feedback):
- Shows current state with professional icons featuring OpenCue logo
- Enhanced status detection (CueBot connectivity, host registration, ping monitoring)
- Allows manual control with intelligent menu states
- Sends notifications with emoji hints (🔒❌⚠️🔧)
- Provides scheduling
- Launches CueGUI directly from tray
- Starts even when CueBot is unreachable and reconnects automatically
Typical setup
- RQD runs as a service: Automatic protection
- CueNIMBY runs at login: Visual feedback and control
State coordination
When RQD locks:
- RQD detects input and locks host
- Cuebot updates host state to NIMBY_LOCKED
- CueNIMBY polls and sees NIMBY_LOCKED
- CueNIMBY updates icon to disabled state (🔒)
- CueNIMBY sends “🔒 NIMBY Locked” notification with emoji hint
When you manually lock via CueNIMBY:
- You uncheck “Available” in menu
- CueNIMBY calls Cuebot API to lock host
- Cuebot updates host state to LOCKED
- Icon changes to red (🔴)
- CueNIMBY sends “Host Disabled” notification
- RQD sees locked state and doesn’t dispatch jobs
Troubleshooting
Icon doesn’t appear
macOS:
- Check System Preferences -> Notifications -> CueNIMBY
- Verify Qt6 is installed
- Try restarting after login
Windows:
- Check system tray settings
- Show hidden icons in overflow area
- Verify Qt6 is installed
Linux:
- Ensure desktop environment supports system tray with Qt6
- Works on GNOME, KDE, XFCE, and other desktop environments
- No AppIndicator required with Qt6
Can’t connect to Cuebot
Symptoms: ❌ Red error icon, “CueBot Unreachable” status
macOS:
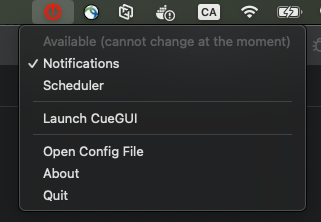
Windows:
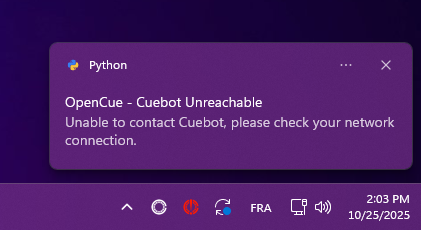
Note: CueNIMBY will now start even when CueBot is unreachable and automatically reconnect when available.
Solutions:
- Check the tray icon tooltip for specific error message
- Verify Cuebot is running:
telnet cuebot.example.com 8443 - Check hostname/port in
~/.opencue/cuenimby.json - Check firewall rules allow gRPC traffic
- Run with
--verboseto see detailed connection errors - CueNIMBY will show clear visual feedback and reconnect automatically
Host not found
Symptoms: ❌ “Machine not found on CueBot, check if RQD is running” status
Solutions:
- Verify RQD is running:
ps aux | grep rqd(macOS/Linux) or Task Manager (Windows) - Check RQD logs for connection errors
- Verify hostname matches in CueBot (check CueGUI > Monitor Hosts)
- Use
--hostnameflag to specify exact hostname - Ensure RQD successfully registered with CueBot
Host lagging
Symptoms: ⚠️ “Host ping above limit” warning icon
macOS:
Windows:
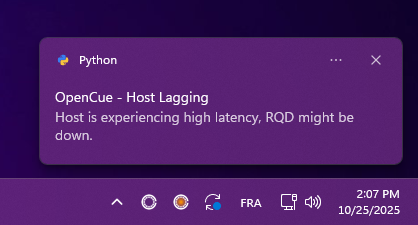
Solutions:
- Check if RQD is still running
- Verify network connection stability
- Review RQD logs for connection issues
- Consider restarting RQD if problem persists
- Check CueBot server load
Host under repair
Symptoms: 🔧 “Under Repair” status icon
macOS:
Windows:
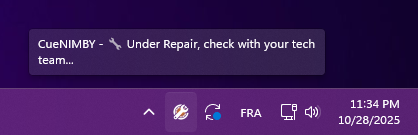
Solutions:
- Contact your technical team for repair status
- Host has been administratively marked for maintenance
- No rendering will occur until repair state is cleared
- Check with system administrators for estimated resolution
Notifications not working
macOS:
- Grant notification permissions in System Preferences
- For best reliability, install terminal-notifier:
brew install terminal-notifier - Alternative: Install
pync:pip install pync - Built-in fallback uses osascript (no additional install required)
Windows:
- Check Windows notification settings
- Install
win10toast:pip install win10toast
Linux:
- Verify notification daemon is running:
ps aux | grep notification - Install
notify2:pip install notify2 - Test manually:
notify-send "Test" "Message"
State not updating
Symptoms: Icon stuck on one color
Solutions:
- Check
poll_intervalin config (increase if too frequent) - Verify host exists in Cuebot: Check CueGUI Hosts view
- Check hostname matches:
hostnamevs config - Restart CueNIMBY
Scheduler not working
Symptoms: State doesn’t change at scheduled time
Solutions:
- Verify
scheduler_enabled: truein config - Check “Scheduler” is checked in menu
- Verify time format is HH:MM (24-hour)
- Check day names are lowercase (monday, tuesday, etc.)
- Restart CueNIMBY after config changes
High CPU usage
Causes: Polling too frequently
Solution: Increase poll interval in config:
{
"poll_interval": 10
}
Best practices
For artists
- Run at startup: Add CueNIMBY to login items for continuous monitoring
- Understand the icons: Learn the icon states and emoji hints (🔒❌⚠️🔧) for quick status recognition
- Use “Launch CueGUI”: Quick access to detailed job information and host management
- Configure schedule: Match your work hours for automatic control
- Check before heavy work: Manually disable if doing intense local work
- Monitor connection status: Watch for ❌ or ⚠️ icons indicating connection issues
- Use “Open Config File”: Easy access to edit settings directly from tray
- Report issues: Help improve the tool by reporting problems
- Communicate: Let others know if you need exclusive use
For administrators
- Deploy to all workstations: Ensure consistent behavior with Qt6-based application
- Document policies: Clear guidelines for users including new features
- Provide support: Help users understand the icon states and troubleshooting
- Monitor usage: Track NIMBY events and connection issues
- Leverage enhanced status detection: Use CueBot connectivity, host registration, and ping monitoring alerts
- Test updates: Verify new versions before deployment
- Educate users: Train on “Launch CueGUI” and “Open Config File” features for self-service
Performance tips
- Use appropriate poll interval (5-10 seconds)
- Disable notifications if not needed
- Use scheduler to reduce manual intervention
- Close CueNIMBY if not using workstation rendering
Advanced usage
Monitoring remote hosts
Monitor a different host:
cuenimby --hostname render-node-01
Useful for:
- Monitoring render nodes from workstation
- Remote administration
- Multi-host management
Multiple instances
Run separate CueNIMBY instances with different configs:
# Terminal 1 - Local host
cuenimby --config ~/.opencue/local.json
# Terminal 2 - Remote host
cuenimby --config ~/.opencue/remote.json --hostname remote-01
Automation
Start CueNIMBY automatically:
macOS (launchd):
Create ~/Library/LaunchAgents/com.opencue.cuenimby.plist
Windows (Task Scheduler): Create task to run on login
Linux (systemd user service):
Create ~/.config/systemd/user/cuenimby.service
Log monitoring
View logs for debugging:
cuenimby --verbose 2>&1 | tee cuenimby.log
Related guides
- Desktop rendering control guide - Understanding desktop allocations, subscriptions, and NIMBY states
- NIMBY concept guide - Overview of NIMBY system components
- Quick start: CueNIMBY - Get started quickly
- CueNIMBY tutorial - Step-by-step tutorial
- CueNIMBY development guide - For developers